Errors during collection, processing and transport of biological specimens are common (Ref: Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 4th Ed).
- Common samples collected are
- Whole blood
- Serum
- Plasma
- Saliva
- Pleural, pericardial, ascitic fluid
- Various types of solid tissues
- Spinal, Synovial, amniotic fluid.
Blood Collection
- Sources – Artery, veins, capillaries
- Venous blood – Venipuncture
- Arterial blood puncture – Arterial blood gas analysis
- Capillaries – Skin puncture, in young children and for point-of-care testing
Venipuncture - Steps
- Confirm identity of the patient – Name, MRD, ward or room number
- Minimum 3 items of identification to be used (International regulations)
- Phlebotomist dressing – Protective equipment, impervious gown and gloves.
- Face mask and goggles needed for patient in isolation rooms.
- Extent of protection varies with type of illness patient has.
- Verify patient condition – Example whether fasting, wherever needed.
- Patient should be comfortably seated or supine for 20 minutes before blood draw. This reduces effects due to hemoconcentration or hemodilution.
- Either arm should be in straight line from shoulder to wrist.
- Contraindications – Indwelling IV line, extensive scarring, hematoma, hand on the side mastectomy was done.
- Estimate volume of blood needed and appropriate number and types of tubes needed, appropriate needles.
- Choice of needles – Adult – G20, collapsable veins – G21, 30-50 ml blood – G18, children G22 or less.
- Sterile, sharp and without barbs.
- For trace elements – Stainless steel. Acid washed apparatus without contamination.
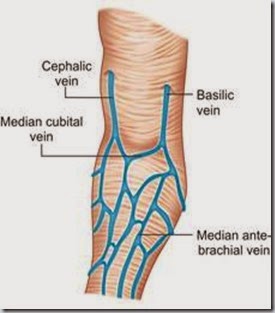
- Location – Median cubital vein in antecubital fossa, crook of elbow preferred site.
- Veins on back of hand, ankle – Next choice, but avoided in diabetics and patients with poor circulation.
- Blood from cannula may be used.
- Any fluid should be shut for 3 minutes before blood draw.
- Blood draw facilitated by palpation of vessel.
- Cleaned with prepackaged alcohol swab or gauze pad saturated with 70% isopropanol.
- Cleaning – Circular motion, site outwards.
- Should be dried in air. Complete drying reduces hemolysis !
- Providone iodine can interfere with biochemistry results and to be avoided !
- For alcohol estimation – Benzalkonium chloride used for cleaning.
- Don’t touch site after cleaning.
- Timing of specimen to be noted.
- Corticosteroids, iron – Diurnal variation
- Monitoring drug therapy.
- Alcohol, drug measurement – Medicolegal considerations.
- Blood pressure cuff ( to 60 mm Hg) or tourniquet (pre-cut soft rubber or Velcro bands) applied 10-15 cm (4-6 inches) above intended site.
- Distends veins making collection easier.
- Changes after 1 min and unacceptable changes after 3 min of tourniquet application.
- First drawn specimen should be used as far as possible, most representative of circulating blood.
- Second tube – 5% and third tube – 10%.
- Prolonged stasis – More than 15% variation.
- If volume is small (large volumes not obtained), prioritize tests.
- Trauma also affects values.
- Pumping of fists to be avoided for
- Potassium
- Phosphate
- Lactate
- Stress can affect values in all ages, especially children, struggling, frightened and physically held back !
- Cortisol
- Growth hormone
- Evacuated blood tubes – Less expensive, more convenient, identified by color code.
- Glass tubes (siliconized) – Reduces hemolysis.
- Blood from one tube not to be transferred to another tube, whatever be the reason.
- Needle gently guided into patient’s vein.
- One needle in place, tube pressed forward to puncture stopper and release vacuum.
- Once blood flows, tourniquet to be released immediately.
- Multiple tubes may be filled with one puncture as needed.
- Shut-off valve may be used if needed.


Special Tubes
- Gel separation tubes
- Polymer gel/silica/lithium heparin
- Serum tubes
- Non-additive, additive
- Whole blood/plasma tubes
- EDTA, citrate, NaF, heparin, oxalate, iodoacetate
- Special chemistry tubes
- Lead, trace elements, stat chemistry
- Plasma preparation tubes
- K-EDTA, polymer gel, silica activator
- Plastic tubes have the advantage of being non-breakable.
- Problems with evacuated tube – Expiry date, short draw related problems.
- Back flow – Sterile tubes to be used, arm to held downwards.
- Blood to be drawn in the order – (1) Blood cultures (2) Non-additive tubes (3) Citrate tubes (4) Serum separator tubes (5) Heparin tubes (6) EDTA and oxalate fluoride tubes.
Tube Codings :
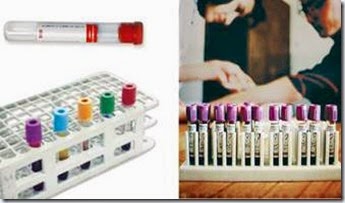
- Non-additive tubes
- Coagulation or citrate containing tube
- Serum separator tube
- Heparin tube
- EDTA
- Oxalate-fluoride
- Red stopper
- Blue
- Red with black flecks
- Green
- Lavender
- Gray stopper
Blood Collection with Syringe
- Needle placed firmly over nozzle of syringe, cover removed.
- Bevel of needle upwards, nozzle downwards.
- Aligned with the vein, 15 degree angle.
- After entering vein, pressure released and blood entered by gently pulling plunger.
- Tube capped with required anti-coagulant.
- Hemolysis – Vigorous suction, forceful transfer from syringe, large-bore needle.
- Patient given dry gauze pad over puncture site, arm raised a bit.
- Needle disposed in sharps container.
- Gloves etc to be disposed in hazardous waste receptacle.
- Venipuncture in children -Similar technique.
- 21G to 23G needle or 20G - 23G butterfly used.
Skin Puncture
- Open collection technique – Skin punctured by lancet.
- Small volume collected into microdevice, capillary tube.
- Indications – (1) Pediatric cases, (2) Severe vein damage, (3) Burns, bandaged patients, (4) POCT cases.
- Sites – Tip of finger, ear lobe, heel or big toe of infants, lateral or medial plantar surface of foot.
- Skin cleaned with gauze pad soaked in 70% isopropanol.
- After drying, quickly punctured by sharp stab with lancet.
- Different site to be used each time.
- Massage to be avoided, as it causes tissue debris accumulation.
- Finger may be warmed, if needed, 3 min before by war, wet cloth.
- First drop discarded. Subsequent drops collected.
- To be rapidly done to avoid clotting. Air bubbles to be avoided.
- Drop by drop collection increases hemolysis.
- Filter paper – Gently touched against large drop of blood, soaked into the paper to fill the marked circle.

- Only single application per circle.
- Complete penetration of paper important.
- Filter papers air dried. Not to be transferred from capillary tubes.
Arterial Puncture
- Requires physicians or trained nurses.
- Preferred sites – (1) Radial artery of wrist, (2) Brachial artery of elbow, (3) femoral artery in groin.
- Neonate – Indwelling catheter in umbilical artery.
- Older child, adult – Capillary puncture to obtain arterialized capillary blood.
- Good for pH, pCO2, but not for pO2.
- Older child, adult – Earlobe, young child or infant – Heel.
- Capillary puncture for arterial blood should be avoided wherever possible.
- Contraindications – Reduced cardiac output, hypotension, vasoconstriction.
- Heparinized capillary tubes containing small metal bar used.
- Tubes filled quickly, contents mixed well by magnet to move metal bar up and down to get uniform specimen.
Anti-coagulants and Preservatives
- Heparin – Least interference except for PCR. High cost, temporary action. Unsuitable for Ca, T3, T4, ACP.
- EDTA – Hematology. Inhibits ALP, CK, LAP, Ca, iron. Reduces cholesterol by 3-5%.
- Sodium fluoride – Glucose. Weak. Inhibits enzymes. Larger amounts needed.
- Citrate – Coagulation studies. Affects enzymes and phosphates.
- Oxalates – Reduces hematocrit, electrolytes, enzymes.
- Iodoacetate – Glucose, urea. Inhibits CK. No effect on other tests.
Effect of Sites
- Skin specimen similar to arterial, dissimilar from venous blood.
- Can be contaminated.
- Central venous catheter – Composition may be affected by infused fluids.
- Blood drawn from central venous catheter and peripheral vein can have different values even if properly collected.
Hemolysis
- Serum shows visible evidence of hemolysis if concentration exceeds 200 mg/L.
- Slight lysis has no effect.
- Severe hemolysis can affect aldolase, ACP, LDH, ICD, K, Mg, phophate in particular.
- Serum protein electrophoresis gives additional band if hemolysis is present.
- Correction for hemoglobin in lysed samples is not accurate for any parameter, hence lysis is undesirable.



No comments:
Post a Comment