TESTING FOR KETONES
The three
ketone bodies are acetone (2%), acetoacetic acid (20%) and 3-β-hydroxybutyrate
(78%). The primary substrates for ketone body formation are free fatty acids
from adipose stores. When glucose is not available ketone bodies supply the
majority of the brains energy. After 3 day fast, ketone bodies provide 30% to
40% of the body’s energy requirements. In uncontrolled diabetes the low insulin
concentrations result in increased lipolysis and decreased reesterification,
thereby increasing plasma free fatty acids. In addition, the increased glucagon:
insulin ratio enhances fatty acid oxidation in
the liver (as seen in type 1
diabetes). Increased counter-regulatory hormones also augment lipolysis and
ketogenesis in adipose tissue and liver respectively. Thus increased hepatic
ketone production and decreased peripheral tissue metabolism lead to
acetoacetate accumulation in the blood. A major fraction is converted to β-hydroxybutyrate.
In healthy people beta hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate are present at
equimolar concentrations, here acetone is minor component. In severe diabetes
the ratio between beta hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate may increase to 6: 1
owing to the presence of large concentration of NADH which favors beta
hydroxybutyrate production. Measurement of ketone bodies is recommended for
patients with type 1 diabetes during acute illness, stress, pregnancy or
elevated blood glucose >300 mg/dL or when the patients has signs of
ketoacidosis.
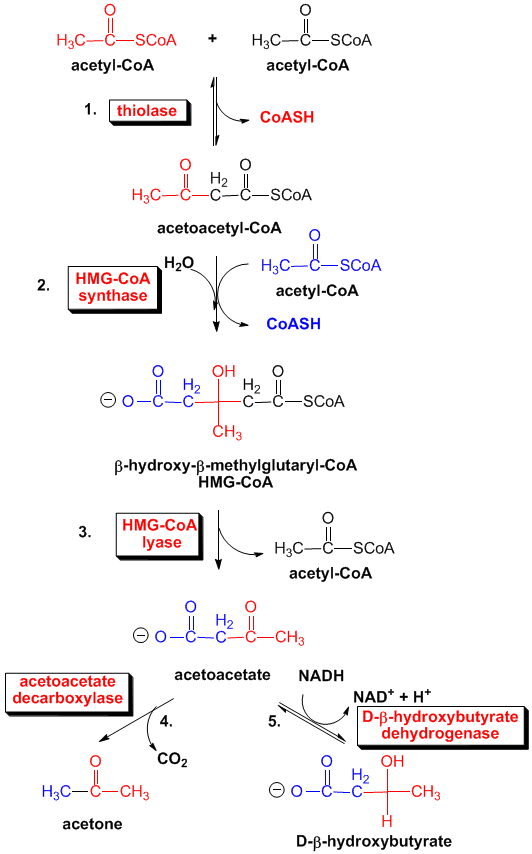 |
| Fig. Ketone bodies Synthesis |
None of the
commonly used methods for the detection and determination of ketone bodies in
serum or urine reacts with all 3 ketone bodies. Gerhardt’s ferric chloride test
reacts with acetoacetate only. Nitroprusside test are least 10 times more
sensitive to acetoacetate than to acetone and give no reaction at all with beta
hydroxybutyrate. So, most of the tests for ketosis essentially detect or
measure acetoacetate only, so presence of ketosis may not be detected. Traditional
tests for beta hydroxybutyrate are indirect; they require brief boiling of the
urine to remove acetone and acetoacetate by evaporation (acetoacetate first
break down spontaneously to acetone) followed by gentle oxidation of beta
hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate and acetone with peroxide, ferric ions or
dichromate. The acetoacetate thus formed
may be detected with Gerhardt’s test or one of the procedures using Nitroprusside.
Excessive
formation of ketone bodies results in increased blood concentrations
(ketonemia) and increased excretion in the urine (ketonuria). This process is
observed in conditions associated with decreased availability of carbohydrates
(like in starvation or frequent vomiting) or decreased use of carbohydrates
(like in diabetes mellitus, glycogen storage disease, von Gierke’s disease and
alkalosis). The popular high-fat, low-carbohydrate diets are ketogenic and
increase ketones in circulation. Diabetes mellitus and alcohol consumption are
the most common cause of ketoacidosis in adults. Ingestion of isopropyl alcohol
and salicylate poisoning can also produce ketoacidosis. Urine ketones are
widely used for monitoring control in patients with type 1 diabetes, pregnancy
with preexisting diabetes and GDM.
Although
quantitative determination of individual ketone bodies is possible these
methods are not used as routine tests. The semiquantitative acetest and
ketostix are frequently used but are insensitive to beta hydroxybutyrate so
negative Nitroprusside test result does not rule out ketoacidosis.
The test
strip contains a mixture of glycine, sodium Nitroprusside, disodium phosphate,
and lactose. Acetoacetate or acetone in the presence of glycine forms a
lavender-purple complex with Nitroprusside.
Beta hydroxyl
butyrate can be determined by using beta hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase to
convert it to acetoacetate with the production of NADH; this NADH is oxidized
to NAD in the presence of NBT and enzyme diaphorase and producing reduced NBT
which is purple compound whose absorbance can be measured.
Urine
testing for ketone bodies are useful for type 1 diabetes mellitus. This testing
is important when glucose levels are persistently higher and associated with
symptoms compatible with ketoacidosis like nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain.
The commercial test uses Nitroprusside-based (Rothras test) reactions to
measure acetoacetate. Certain drugs may cause positive results like captopril
and levodopa, while ascorbic acid intake may cause false negative results.

It is your good blog and technology.So i Ike it as a professional article.Thanks a lot.
ReplyDeletePhospholipase D Assay Kit